We live in an era where the definition of reality evolves with each advancement in the human-machine interface. Technology is advancing thousand times faster than human beings with the latest of technologies becoming obsolete in the quickest of times. Within the last decade, humans were introduced to various technological innovations such as Microsoft’s HoloLens, Facebook and Oculus’ VR, and Google’s Glass and Cardboard, among many others.
Many may be of the thinking that we are nearing the end of technological evolution; however, this is just the beginning of a much longer journey. It hasn’t been too long since VR (Virtual Reality), AR (Augmented Reality), and MR (Mixed Reality) were introduced to us, and there’s already a newcomer known as XR (Extended Reality).
What Is Extended Reality?
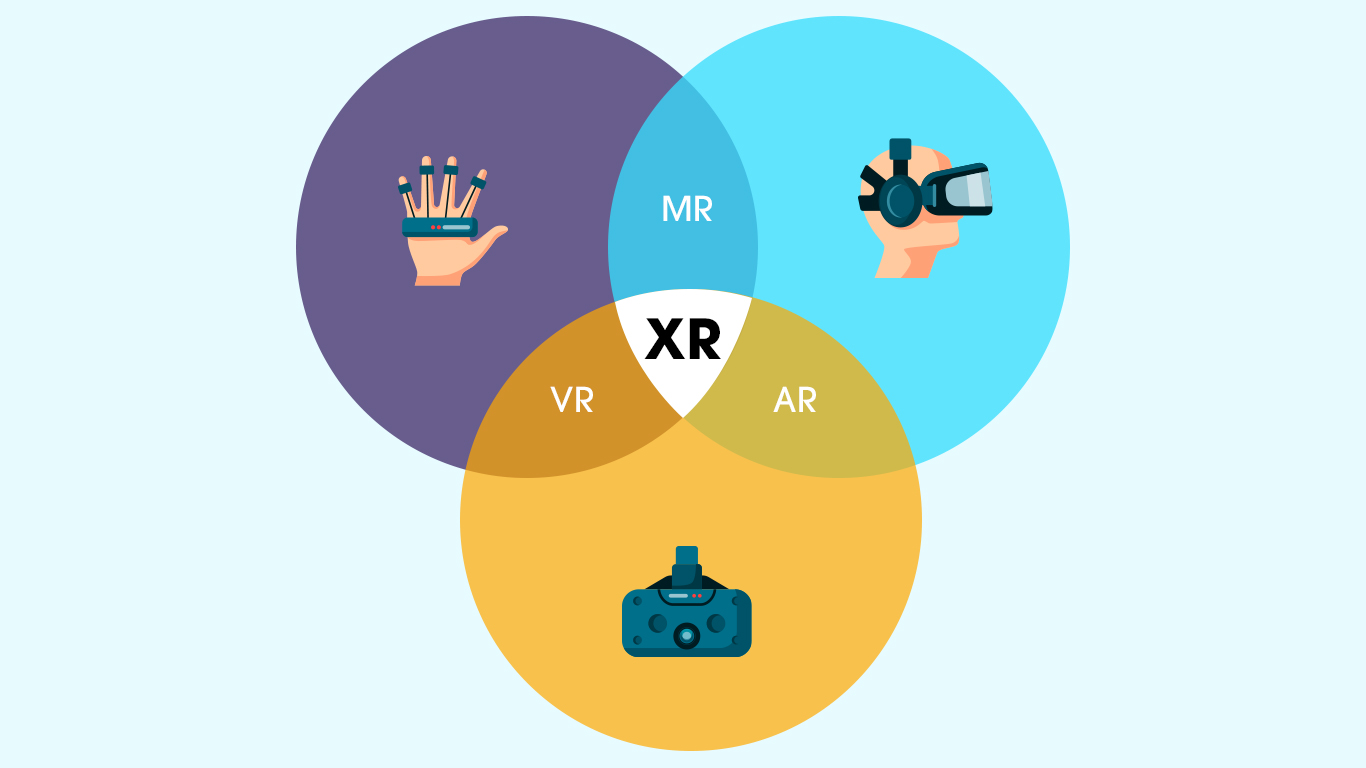
Extended Reality is the term used when referring to the use of a combination of real and virtual environments via wearables and computer technology generated human-machine interactions. It covers the entire spectrum of real and virtual environments. To many, XR is defined as a term that enhances existing technologies such as AR, MR, and VR; however, in actuality, MR, VR, and AR form the three pillars of XR.
Extended Reality combines the features of these three technologies to form one superior technological experience for users. The scope of XR is not limited to the current form of these three technologies and will increase with time and technological innovations in mixed, augmented, and virtual reality.
Types of Extended Reality
While many are of the opinion that Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are the three types of extended reality, practically speaking, they aren’t. Each of these form Extended Reality and aren’t its subtypes. However, here are the exact meanings of AR, VR, and MR.
-
Augmented Reality (AR)
 In Augmented Reality, objects and virtual information are overlaid on the real world. It creates a real-world experience with the addition of digital details such as images, text, and animation. The most renowned example of AR would be the game Pokémon GO, which overlays digital creatures (Pokémon) onto the real world. Another example would be Snapchat filters that put glasses onto a face digitally.
In Augmented Reality, objects and virtual information are overlaid on the real world. It creates a real-world experience with the addition of digital details such as images, text, and animation. The most renowned example of AR would be the game Pokémon GO, which overlays digital creatures (Pokémon) onto the real world. Another example would be Snapchat filters that put glasses onto a face digitally.
-
Virtual Reality (VR)
 Contrary to AR, in a Virtual Reality experience, users are completely immersed in a digitally simulated environment. This requires users to utilize a VR headset to get a 360-degree view of an artificial world. The gaming industry is one of the pioneers of this technology and also one of the earliest adopters of it. Other industries that leverage VR are healthcare, construction, military, and engineering, among others.
Contrary to AR, in a Virtual Reality experience, users are completely immersed in a digitally simulated environment. This requires users to utilize a VR headset to get a 360-degree view of an artificial world. The gaming industry is one of the pioneers of this technology and also one of the earliest adopters of it. Other industries that leverage VR are healthcare, construction, military, and engineering, among others.
-
Mixed Reality (MR)
 The Mixed Reality concept combines both digital and real-world objects and enables real-time interaction. It is the latest immersive technology and is also referred to as hybrid reality. Mixed Reality needs users to wear an MR headset, such as Microsoft’s HoloLens. Companies, worldwide, are currently trying to explore the different ways in which they can utilize MR to solve problems, improve businesses, and support initiatives.
The Mixed Reality concept combines both digital and real-world objects and enables real-time interaction. It is the latest immersive technology and is also referred to as hybrid reality. Mixed Reality needs users to wear an MR headset, such as Microsoft’s HoloLens. Companies, worldwide, are currently trying to explore the different ways in which they can utilize MR to solve problems, improve businesses, and support initiatives.
Advantages of Extended Reality
Listed below are some of the numerous advantages that XR provides users with
- Provides a unique and unmatched experience
- Increases accessibility
- Provides users with a realistic view and enables more effective training
- Increases user safety in training areas such as the military, or professions such as pilots, or chemists
- Does away with distance barriers and allows smoother access to remote data
- Saves time, money, and resources as it provides users interaction anywhere
- Enhances learning experience and generates skilled human capital
Disadvantages of Extended Reality
With all of the advantages that this technology provides, there are a few areas of concern, and these are mentioned below.
- As it is based on a computer network, the threat of cyber hacks and attacks is imminent
- In providing users with easy access, it reduces the social engagement of users
- May affect eyes if used for long periods of time, and in some cases, headaches or migraines
- Involves the use of multiple devices, which increases implementation costs
- Since XR is pre-programmed, it requires expert supervision in some cases, which reduces the flexibility of XR for the common man
Extended Reality Industry Applications and Use Cases
-
Healthcare
 Medical imaging leverages Extended Reality extensively in modern MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans. Extended Reality provides healthcare professionals with a 3D representation of their scan as compared to the outdated 2D imaging technologies. XR enhances diagnostic efficiency and considerably expands surgical training opportunities for students. Companies such as Philips, GE Healthcare, and Siemens have been implementing these technologies into their machines to stay ahead of their competition.
Medical imaging leverages Extended Reality extensively in modern MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans. Extended Reality provides healthcare professionals with a 3D representation of their scan as compared to the outdated 2D imaging technologies. XR enhances diagnostic efficiency and considerably expands surgical training opportunities for students. Companies such as Philips, GE Healthcare, and Siemens have been implementing these technologies into their machines to stay ahead of their competition.
-
Real Estate
 Extended Reality has come as a boon to real estate agencies as it allows potential customers to view properties without actually going to the place. It is a huge time-saver for all the involved parties and reduces the stress related to the property selection process. Other than just the basics, in architecture and interior design, Extended Reality allows professionals to put the onus of designing their property their way. For instance, Houzz, a design company, utilized AR to enables its customers to imagine their future furnishings. By way of an online app, users get ideas for home improvement. Another plus is that Houzz claims that the app increases purchase probability by 11x!
Extended Reality has come as a boon to real estate agencies as it allows potential customers to view properties without actually going to the place. It is a huge time-saver for all the involved parties and reduces the stress related to the property selection process. Other than just the basics, in architecture and interior design, Extended Reality allows professionals to put the onus of designing their property their way. For instance, Houzz, a design company, utilized AR to enables its customers to imagine their future furnishings. By way of an online app, users get ideas for home improvement. Another plus is that Houzz claims that the app increases purchase probability by 11x!
-
Manufacturing
 A large manufacturer of mining, utility, and construction equipment, Komatsu, leverages Extended Reality for the purpose of training their equipment operators. This significantly reduces the losses caused due to the improper use of expensive machines by providing training to their operators worldwide.
A large manufacturer of mining, utility, and construction equipment, Komatsu, leverages Extended Reality for the purpose of training their equipment operators. This significantly reduces the losses caused due to the improper use of expensive machines by providing training to their operators worldwide.
-
Gaming
 Well, the list would be truly incomplete without this sector, and here it is. Extended Reality is here to change the definition of entertainment and how people game. The video game sector is slated to benefit the most from XR implementation. Along with a live video gaming experience, Extended Reality will also enhance entertainment events such as concerts, football, and cricket matches, and much more. For instance, the Denver Museum of nature and science is already making use of Extended Reality to improve the overall visitor experience.
Well, the list would be truly incomplete without this sector, and here it is. Extended Reality is here to change the definition of entertainment and how people game. The video game sector is slated to benefit the most from XR implementation. Along with a live video gaming experience, Extended Reality will also enhance entertainment events such as concerts, football, and cricket matches, and much more. For instance, the Denver Museum of nature and science is already making use of Extended Reality to improve the overall visitor experience.
Extended Reality in Business
As an option, businesses can choose whether they want and need to apply Extended Reality technology. It comes with valuable advantages for businesses, and many brands have already started leveraging it. While Extended Reality provides multiple benefits, it is still a little risky and requires brands to invest significantly.
Brands need to be wary about a few aspects that come along with XR. First off, brands must have a robust data security structure in place as cyber-attacks and hacks adversely affect business. Profiteering with XR, without data security, is a myth. Next is the choice of the service provider. Businesses need to choose a reliable service provider, which really is half the battle in XR implementation, as unaddressed system breakdowns and malfunctions lead to interruptions in the business cycle.
Conclusion
Technology is being developed at an unprecedented pace, and the public is more than willing to give it a go and adopt it once it is available in the market. Extended Reality, without a shadow of a doubt, has plenty of areas and fields where it can be used such as retail, real estate, training, marketing, and entertainment, among others. Extended Reality can, additionally, be used by the most sophisticated of UI UX design services. It possesses the capability to completely alter the way we go about our day-to-day lives as it will change our perception of reality.
